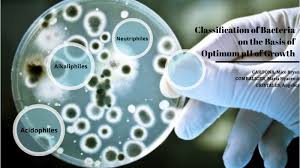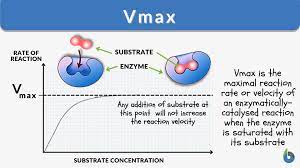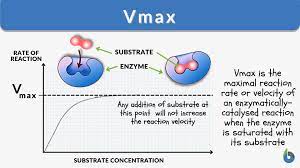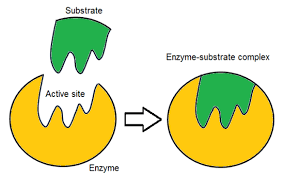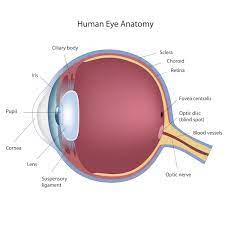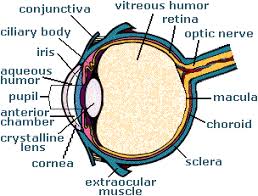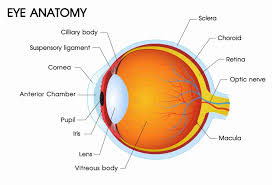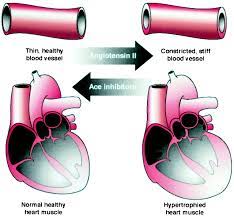
INHIBITORS :
Inhibitors block the active site temporarily or permanently. • Examples: poisons like cyanide, antibodies, anti-metabolites, pesticides and some drugs. Types of Enzyme Inhibitors: The inhibitors can be divided into two types. (i) Irreversible inhibitors (ii)